

Lysine has Guanidinium group in the ‘R’ side chain of Lysine.Substantial efforts to avoid developability risks are now more often being made during the candidate discovery, engineering, and lead optimization phases of biotherapeutic development. The isoelectric point of the Lysine is 9.7 According to isoelectric point concept, the given formula will be applied: Calculate the Isoelectric point of Lysine? (pK1 = 2.2, pK2=8.9 pK3=10.5)Īns: Lysine is basic amino acids (diamino monocarboxylic acid).
The isoelectric point of the Glycine is 6.1Ģ. According to isoelectric point concept, the given formula will be applied Calculate the Isoelectric point of Glycine? (pK1=2.4 pK2=9.8)Īns: Glycine is a neutral and optically inactive amino acid. PK3=Dissociation (or) Association constant of “R” side chain Problems and Solutions on Zwitter ion and Isoelectric Pointġ. PK1=Dissociation constant of (-COOH) group
#Calculate pi isoelectric point free
The amino acids rarely exist in a neutral form with free carboxyl (-COOH) and free amino (-NH2) groups.
Basically the proton shifts from carboxyl group to amino group of the self-molecule at normal pH cellular levels.

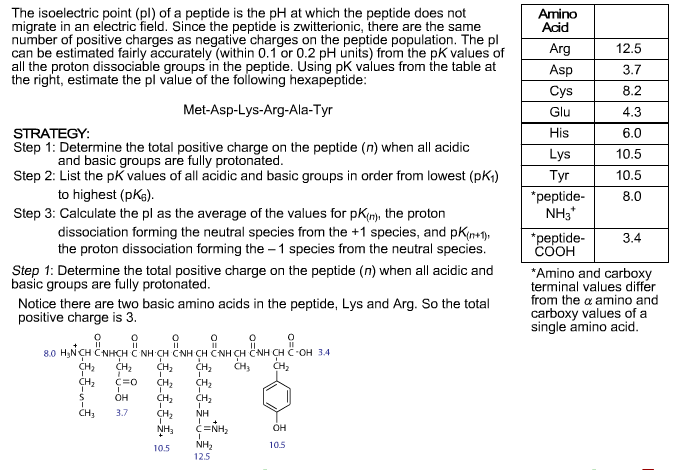
Zwitterion (or) dipolar ion is a hybrid molecule containing positive & negatively ionic groups. The name zwitter is derived from the German word which means “hybrid”. Thus, dicarboxylic acid like glutamic acid can have three pK values (two for carboxyl groups and one for the amino group) and four types of charged molecules as shown below. Similarly, when the pH is further raised to around 9.8 the amino group is dissociated – this pH is called the pK of an amino group. This is called the pK of the acid group and at this pH, dissociated and undissociated species are found in equal concentrations. However when the pH is raised and reaches around pH 3.0, the proton from the carboxyl group is leaving a -COO- group. In Strong acid conditions (around pH 1.1) the alpha-COOH group remains undissociated. Problems and Solutions on Zwitter ion and Isoelectric Point.Solubility and buffering capacity will be minimum at isoelectric pH.Isoelectric Points of Some Important Proteins:.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
